What is an Aneurysm?
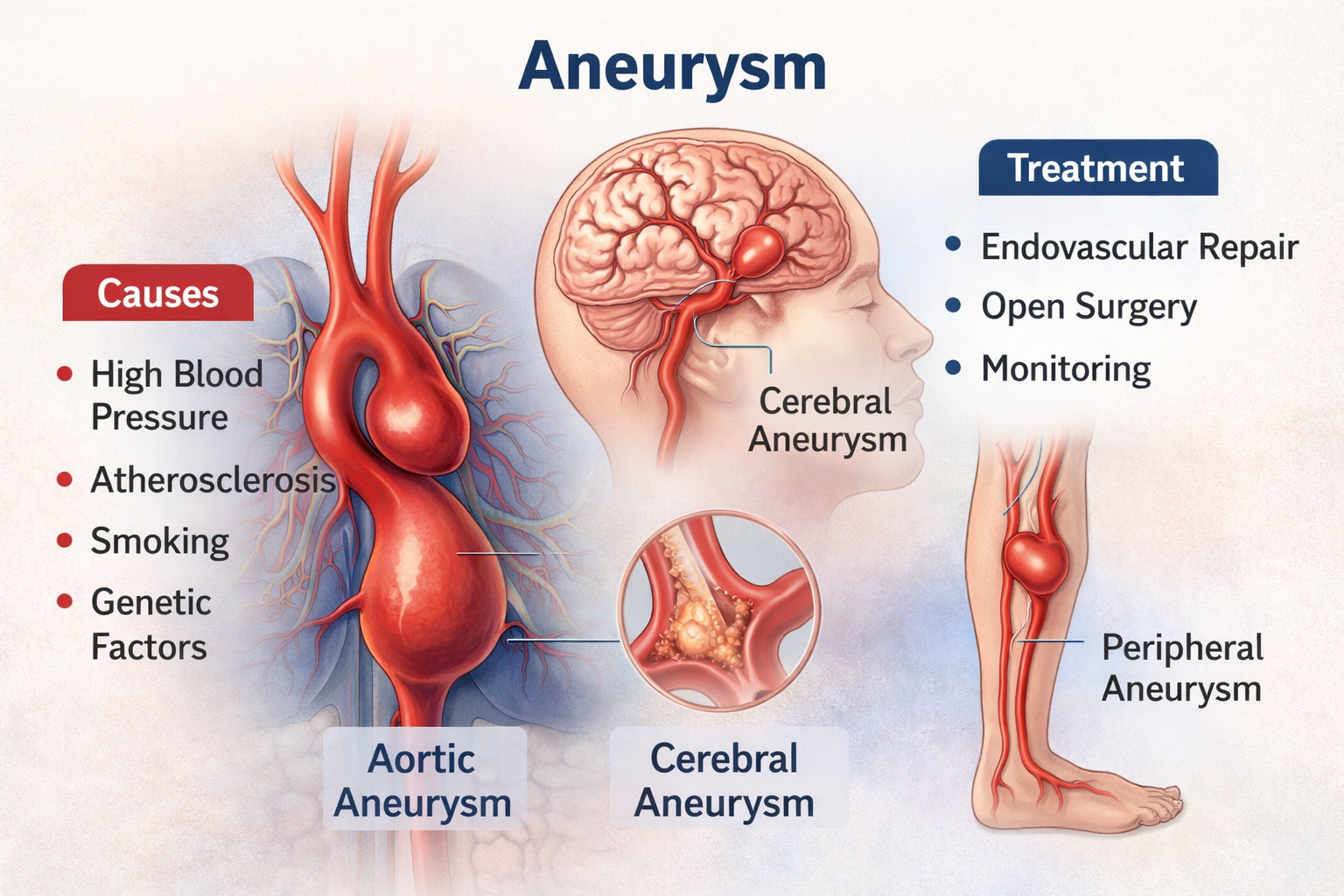
An aneurysm is a serious vascular condition in which a blood vessel wall becomes weak and bulges outward like a balloon. It can occur in different parts of the body, most commonly in the aorta (aortic aneurysm), brain (cerebral aneurysm), or peripheral arteries such as the popliteal artery. If left untreated, an aneurysm can enlarge and may rupture, leading to life-threatening internal bleeding.
Early detection and proper vascular evaluation are essential to prevent complications.
Types of Aneurysm
-
Aortic Aneurysm
-
Thoracic Aneurysm (chest area)
-
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA)
-
-
Peripheral Aneurysm
-
Popliteal artery aneurysm (behind the knee)
-
Femoral artery aneurysm
-
-
Cerebral Aneurysm
-
Occurs in blood vessels of the brain
-
Causes of Aneurysm
Several factors can weaken artery walls and increase the risk of aneurysm formation:
-
Atherosclerosis (plaque buildup in arteries)
-
High blood pressure (hypertension)
-
Smoking
-
Genetic predisposition
-
Trauma or infection
-
Connective tissue disorders
Controlling risk factors significantly reduces complications.
Symptoms of Aneurysm
Many aneurysms do not cause symptoms in early stages and are detected incidentally during imaging tests. However, larger aneurysms may cause:
-
Chest or back pain (thoracic aneurysm)
-
Abdominal pain or pulsating mass (AAA)
-
Leg pain or swelling (peripheral aneurysm)
-
Sudden severe pain if rupture occurs
A ruptured aneurysm is a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment.
Diagnosis
Aneurysms are diagnosed using advanced imaging techniques such as:
-
Ultrasound
-
CT Angiography (CTA)
-
MRI
-
Doppler studies
Regular screening is advised for high-risk individuals, especially smokers and patients with hypertension.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the size, location, and risk of rupture.
1. Monitoring (Small Aneurysms)
Small aneurysms may only require regular follow-up and blood pressure control.
2. Open Surgical Repair
The weakened artery section is replaced with a synthetic graft.
3. Endovascular Repair (Minimally Invasive)
A stent graft is placed inside the artery through a small incision to reinforce the vessel wall. This method usually offers faster recovery and less post-operative discomfort.
When to See a Vascular Specialist?
If you experience persistent chest pain, abdominal discomfort, leg swelling, or have high-risk factors such as long-term smoking or hypertension, consult a vascular specialist immediately. Early intervention can prevent rupture and save lives.
Expert Vascular Care in Delhi NCR
Advanced diagnosis and treatment for aneurysm are available at Vascular Surgery Delhi under the expertise of a senior vascular and endovascular surgeon. Modern minimally invasive techniques ensure safe and effective outcomes with quicker recovery.